Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Enzyme Classification
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in the body. They are classified into six main categories based on the type of reaction they catalyze: oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. Understanding this classification is essential for identifying the specific type of enzyme involved in the conversion of ethylene glycol to its toxic metabolites.
Recommended video:
Six Main Classifications Concept 3
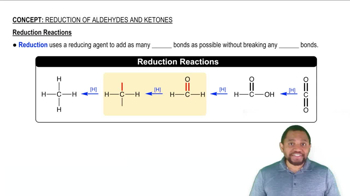
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions involve the transfer of electrons between molecules, leading to changes in their oxidation states. In the metabolism of ethylene glycol, the conversion to oxoethanoic acid and subsequently to oxalic acid involves redox processes, typically catalyzed by oxidoreductases. Recognizing these reactions is crucial for understanding the enzymatic pathways involved in the toxicity of ethylene glycol.
Recommended video:
Reduction Reactions Concept 1
Toxic Metabolites
Toxic metabolites are harmful byproducts formed during the metabolism of substances in the body. In the case of ethylene glycol, its metabolism leads to the formation of oxalic acid, which can cause metabolic acidosis and kidney damage. Understanding the nature and effects of these toxic metabolites is vital for assessing the risks associated with ethylene glycol ingestion and the role of enzymes in their production.
Recommended video:
Gluconeogenesis Concept 12
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 :39m
:39m