Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electrolytes
Electrolytes are substances that dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, allowing the solution to conduct electricity. They are classified into strong electrolytes, which completely dissociate into ions, weak electrolytes, which partially dissociate, and nonelectrolytes, which do not dissociate at all. Understanding these classifications is essential for analyzing solute behavior in aqueous solutions.
Recommended video:
Electrolytes (Simplified) Example 3
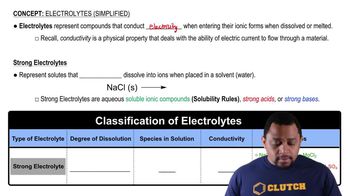
Strong Electrolytes
Strong electrolytes are compounds that fully dissociate into their constituent ions in solution. Examples include soluble salts like potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄), which dissociates completely into 2K⁺ and SO₄²⁻ ions in water. This complete dissociation is crucial for understanding the conductivity and chemical behavior of solutions.
Recommended video:
Electrolytes (Simplified) Concept 1
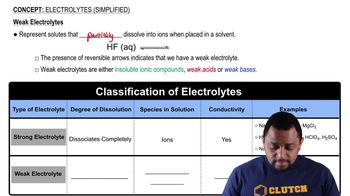
Weak Electrolytes
Weak electrolytes are substances that only partially dissociate into ions in solution, resulting in a mixture of ionized and non-ionized molecules. Common examples include acetic acid and ammonia. The degree of dissociation affects the solution's conductivity and pH, making it important to distinguish between weak and strong electrolytes in chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Electrolytes (Simplified) Concept 2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution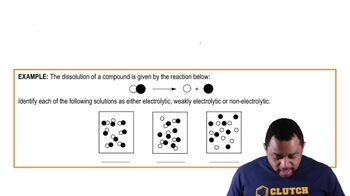

 2:38m
2:38m