Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, specifically glucose, using carbon dioxide and water. This process occurs in chloroplasts and involves two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. It is endergonic, meaning it requires energy input, primarily from sunlight.
Oxidation
Oxidation refers to the chemical process in which a substance loses electrons, often associated with the release of energy. In biological systems, oxidation typically involves the breakdown of glucose during cellular respiration, which is an exergonic process that releases energy. This energy is then used to fuel various cellular activities.
Recommended video:
Oxidation of Monosaccharides Concept 1
Exergonic and Endergonic Reactions
Exergonic reactions are those that release energy, making them spontaneous and often associated with processes like oxidation. In contrast, endergonic reactions require an input of energy to proceed, such as photosynthesis. Understanding the energy dynamics of these reactions is crucial for analyzing metabolic pathways and their interconnections.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution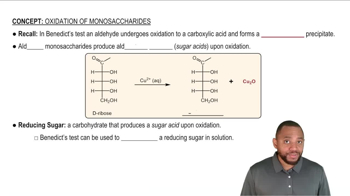


 1:23m
1:23m