Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidoreductases
Oxidoreductases are a class of enzymes that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions, where the transfer of electrons occurs between molecules. These enzymes play a crucial role in metabolic pathways, facilitating the conversion of substrates by either adding or removing electrons. NAD+ and FAD serve as essential coenzymes in these reactions, acting as electron carriers that help in the oxidation of substrates.
Recommended video:
Oxidoreductases Example 3
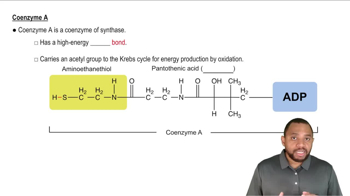
Coenzymes
Coenzymes are organic non-protein molecules that assist enzymes in catalyzing reactions. They often act as carriers for chemical groups or electrons during enzymatic reactions. NAD+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and FAD (Flavin adenine dinucleotide) are two vital coenzymes that participate in redox reactions, enabling the transfer of electrons and protons, which is essential for cellular respiration and energy production.
Recommended video:
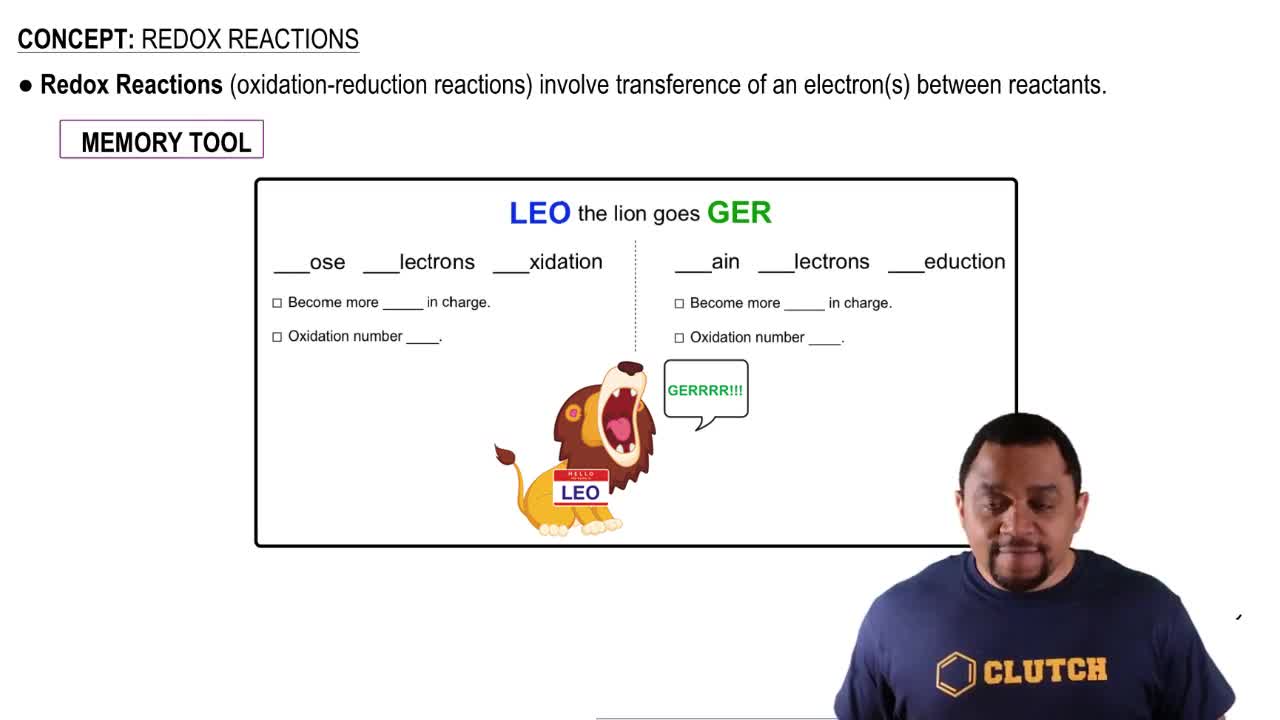
Redox Reactions
Redox reactions, short for reduction-oxidation reactions, involve the transfer of electrons between two species. In these reactions, one molecule is oxidized (loses electrons) while another is reduced (gains electrons). The coenzymes NAD+ and FAD are integral to these processes, as they accept electrons during oxidation and release them during reduction, thus facilitating energy transfer within biological systems.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 2:23m
2:23m