Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Fatty Acyl CoA
Fatty acyl CoA is a fatty acid that has been activated by the addition of coenzyme A (CoA). This activation is crucial for the subsequent β-oxidation process, as it allows the fatty acid to enter the mitochondria for energy production. The formation of fatty acyl CoA involves the enzyme acyl-CoA synthetase, which catalyzes the reaction using ATP.
Recommended video:
Oxidation of Fatty Acids Concept 2
β-Oxidation
β-oxidation is the metabolic process by which fatty acids are broken down in the mitochondria to generate acetyl-CoA, NADH, and FADH2. This process occurs in a series of enzymatic reactions that sequentially remove two-carbon units from the fatty acid chain. It is essential for energy production, especially during periods of fasting or intense exercise.
Recommended video:
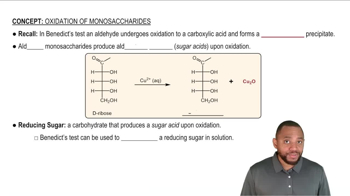
Oxidation of Monosaccharides Concept 1
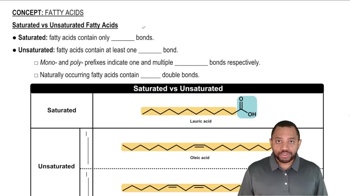
Saturated Fatty Acids
Saturated fatty acids are types of fatty acids that contain no double bonds between carbon atoms in their hydrocarbon chain, meaning they are 'saturated' with hydrogen atoms. Lauric acid, specifically, is a 12-carbon saturated fatty acid found in coconut oil. Its structure influences its physical properties and metabolic pathways, including its role in energy production through β-oxidation.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution

 1:29m
1:29m