Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkyl Groups
Alkyl groups are derived from alkanes by removing one hydrogen atom, resulting in a hydrocarbon chain. In the given compound, CH₃−CH₂− and CH₂−CH₂−CH₃ represent two alkyl groups, ethyl and propyl, respectively. Understanding alkyl groups is essential for naming organic compounds and recognizing their structure.
Recommended video:
Ether Functional Group
An ether is a class of organic compounds characterized by an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. The general structure is R−O−R', where R and R' are the hydrocarbon chains. In the provided compound, the presence of the oxygen atom between the two alkyl groups indicates that it is an ether, specifically diethyl ether.
Recommended video:
Functional Group Priorities Concept 1
IUPAC Nomenclature
IUPAC nomenclature is a systematic method for naming organic chemical compounds. It provides rules for identifying the structure and functional groups within a molecule, allowing for a standardized name. For the compound CH₃−CH₂−O−CH₂−CH₂−CH₃, applying IUPAC rules helps in determining its common name, which is diethyl ether.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution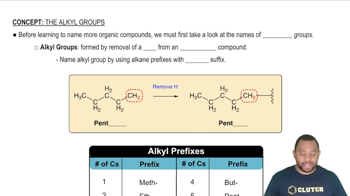



 :34m
:34m