Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkenes
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C). They are unsaturated compounds, meaning they have fewer hydrogen atoms than alkanes with the same number of carbon atoms. The presence of the double bond gives alkenes unique reactivity, making them important in various chemical reactions, including addition reactions where new atoms or groups can be added across the double bond.
Recommended video:
Aldehydes and Ketones
Aldehydes and ketones are both carbonyl compounds characterized by the presence of a carbon-oxygen double bond (C=O). Aldehydes have the carbonyl group at the end of the carbon chain, while ketones have it within the chain. These functional groups significantly influence the chemical properties and reactivity of the compounds, making them key players in organic synthesis and various chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
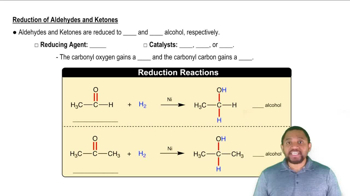
Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones Concept 2
Condensed Structural and Line-Angle Formulas
Condensed structural formulas provide a simplified representation of a molecule, showing the arrangement of atoms without depicting all bonds explicitly. Line-angle formulas, on the other hand, use lines to represent bonds between atoms, with vertices representing carbon atoms. Both methods are essential for visualizing organic compounds and understanding their structure, which is crucial for predicting reactivity and properties in chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Condensed Formula Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:3m
1:3m