Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Citric Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, is a series of enzymatic reactions that occur in the mitochondria, playing a crucial role in cellular respiration. It involves the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, leading to the production of energy carriers like NADH and FADH2, which are essential for ATP synthesis.
Recommended video:
Citric Acid Cycle Summary Concept 12
Oxidation Reactions
Oxidation reactions involve the loss of electrons from a molecule, often accompanied by the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen. In the context of the citric acid cycle, these reactions are critical for energy production, as they facilitate the conversion of substrates into energy-rich molecules, contributing to the overall metabolic pathway.
Recommended video:
Alcohol Reactions Oxidation Reactions Example 1
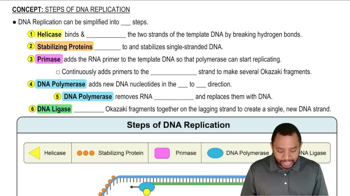
Enzymatic Steps
The citric acid cycle consists of eight distinct enzymatic steps, each catalyzed by specific enzymes that facilitate the conversion of substrates through various chemical transformations. Understanding which steps involve oxidation is essential for grasping how energy is extracted from organic molecules and how metabolic pathways are interconnected.
Recommended video:
Steps of DNA Replication Concept 1
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution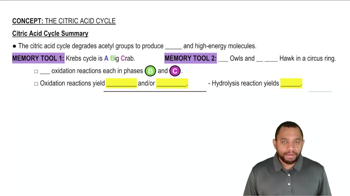


 :50m
:50m