Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Fatty Acid Oxidation
Fatty acid oxidation is the metabolic process by which fatty acids are broken down to produce energy. This process occurs in the mitochondria and involves the sequential removal of two-carbon units from the fatty acid chain, ultimately converting them into acetyl-CoA, which can enter the citric acid cycle for further energy production.
Recommended video:
Oxidation of Fatty Acids Concept 3
Beta Oxidation
Beta oxidation specifically refers to the series of enzymatic reactions that occur during the oxidation of fatty acids. It is named 'beta' because the oxidation occurs at the beta carbon, which is the second carbon atom adjacent to the carboxyl group of the fatty acid. This process is crucial for the efficient utilization of fatty acids as an energy source.
Recommended video:
Energy Yield
The energy yield from beta oxidation is significant, as it produces multiple molecules of acetyl-CoA, NADH, and FADH2 from each fatty acid molecule. These products are vital for ATP production in cellular respiration, making fatty acids a dense energy source compared to carbohydrates and proteins, which is why understanding beta oxidation is essential in biochemistry and metabolism.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution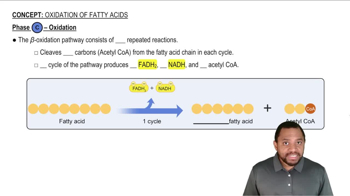



 1:29m
1:29m