Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius. It is a crucial property that determines how a material responds to heat. Substances with high specific heat can absorb more heat without a significant change in temperature, while those with low specific heat heat up quickly.
Recommended video:
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity refers to a material's ability to conduct heat. It influences how quickly heat is transferred through a substance. In the context of sand and water, the difference in thermal conductivity helps explain why sand heats up quickly in the sun, while water remains cooler, as water has a higher capacity to absorb heat without a rapid increase in temperature.
Recommended video:
Thermal Equilibrium (Simplified) Concept 1
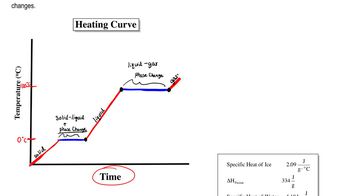
Phase Change and Heat Absorption
Phase change refers to the transition of a substance from one state of matter to another, such as from liquid to gas. During these changes, substances can absorb or release significant amounts of heat without changing temperature. Water, for instance, has a high latent heat of vaporization, allowing it to absorb heat energy effectively, which contributes to its cooler temperature compared to sand on a hot day.
Recommended video: