Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction that involves the addition of hydrogen (H2) to a compound, typically an unsaturated hydrocarbon. In the case of alkynes, this process converts the triple bond into a single bond, resulting in the formation of alkanes. This reaction is often facilitated by catalysts such as palladium, platinum, or nickel, which help speed up the reaction without being consumed.
Recommended video:
Hydrogenation Reactions Concept 1
Alkynes
Alkynes are a class of hydrocarbons characterized by at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. They are unsaturated compounds, which means they have fewer hydrogen atoms than alkanes or alkenes. The general formula for alkynes is CnH2n-2, where 'n' is the number of carbon atoms. Common examples include ethyne (acetylene) and propyne.
Recommended video:
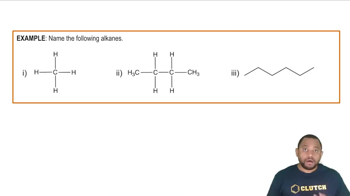
Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds between carbon atoms, following the general formula CnH2n+2. They are less reactive than alkenes and alkynes due to the absence of double or triple bonds. Alkanes are typically found in natural gas and petroleum, and they serve as important fuels and feedstocks in the chemical industry.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 1:22m
1:22m