Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkenes
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond (C=C). They are unsaturated compounds, meaning they have fewer hydrogen atoms than alkanes with the same number of carbon atoms. Alkenes are reactive and can undergo various chemical reactions, including addition reactions, where other atoms or groups are added across the double bond.
Recommended video:
Addition Reactions
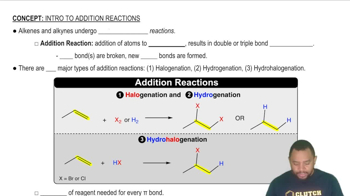
Addition reactions are a type of chemical reaction where two or more reactants combine to form a single product. In the context of alkenes, these reactions often involve the addition of halogens, hydrogen, or water across the double bond. Understanding the specific conditions and reagents required for these reactions is crucial for predicting the products formed from a given alkene.
Recommended video:
Addition Reactions Concept 1
Reagents
Reagents are substances that are added to a chemical reaction to cause a transformation. In the case of alkenes, common reagents include hydrogen (for hydrogenation), halogens (for halogenation), and acids (for hydration). Identifying the correct reagent is essential for determining the products of the reaction and understanding the mechanism involved.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 :56m
:56m