Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
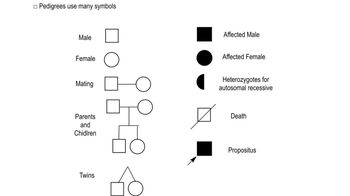
Pedigrees
Problem 14c
Textbook Question
Nail–patella syndrome is an autosomal disorder affecting the shape of nails on fingers and toes as well as the structure of kneecaps. The pedigree below shows the transmission of nail–patella syndrome in a family along with ABO blood type. Is nail–patella syndrome a dominant or a recessive condition? Explain your reasoning.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
<Step 1: Understand the genetic basis of the disorder. Nail–patella syndrome is an autosomal disorder, meaning the gene responsible is located on one of the non-sex chromosomes.>
<Step 2: Analyze the pedigree. Look for patterns in the inheritance of the disorder across generations.>
<Step 3: Identify if the disorder appears in every generation. If it does, this suggests a dominant pattern. If it skips generations, it may be recessive.>
<Step 4: Check if affected individuals have at least one affected parent. In a dominant disorder, affected individuals typically have an affected parent.>
<Step 5: Consider the possibility of new mutations or incomplete penetrance, which can sometimes complicate the analysis of pedigrees.>
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Autosomal Dominance and Recessiveness
Autosomal dominance refers to a pattern of inheritance where only one copy of a mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the disorder. In contrast, autosomal recessiveness requires two copies of the mutated gene for the condition to manifest. Understanding these patterns is crucial for analyzing pedigree charts and determining the inheritance of traits.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Variations on Dominance
Pedigree Analysis
A pedigree chart is a visual representation of a family's genetic history, showing how traits are passed through generations. By examining the presence or absence of a condition in family members, one can infer whether a trait is dominant or recessive. This analysis helps identify carriers and predict the likelihood of the condition appearing in future generations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Pedigree Flowchart
ABO Blood Type Genetics
The ABO blood type system is determined by the presence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells, which are inherited in a codominant manner. Understanding blood type inheritance can provide additional context in pedigree analysis, as it may help differentiate between individuals with similar phenotypes and clarify the genetic relationships within the family.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Descriptive Genetics

 2:48m
2:48mWatch next
Master Pedigree Symbols with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning