Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Mapping Genes
Problem 23a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionHow do we know that in humans the X chromosomes play no role in human sex determination, while the Y chromosome causes maleness and its absence causes femaleness? Why are many expected crossover phenotypes missing? Can any of these loci be mapped from the data given here? If so, determine map distances.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
4mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Sex Chromosome Function
In humans, sex determination is primarily influenced by the presence of the Y chromosome. The SRY gene located on the Y chromosome triggers male development, while its absence leads to female development. The X chromosomes carry genes that are not directly involved in determining sex but are essential for various biological functions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Human Sex Chromosomes
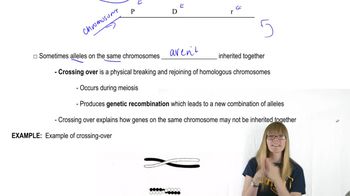
Crossover and Genetic Mapping
Crossover refers to the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during meiosis, which can result in new allele combinations. Missing expected crossover phenotypes can occur due to genetic linkage, where genes are located close together on the same chromosome, reducing the likelihood of recombination. Genetic mapping involves determining the distance between loci based on crossover frequencies.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Mapping Overview
Map Distance Calculation
Map distance is a measure of the relative distance between genes on a chromosome, typically expressed in centimorgans (cM). It is calculated based on the frequency of recombination events; a higher frequency indicates greater distance. By analyzing the data from crossover events, one can estimate the map distances between loci, aiding in the understanding of genetic linkage and inheritance patterns.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping Genes
Related Videos
Related Practice




