Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
Bacteriophage Genetics
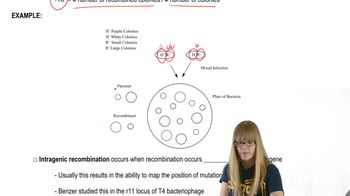
Problem 17
Textbook Question
In recombination studies of the rII locus in phage T4, what is the significance of the value determined by calculating phage growth in the K12 versus the B strains of E. coli following simultaneous infection in E. coli B? Which value is always greater?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the context: The rII locus in phage T4 is used to study genetic recombination. Phage T4 can infect different strains of E. coli, such as K12 and B.
Identify the experimental setup: Phage T4 is used to infect E. coli B, and the resulting phages are then tested for their ability to grow on E. coli K12 and E. coli B.
Recognize the significance of the strains: E. coli B allows for the growth of all phage types, while E. coli K12 only allows growth of recombinant phages that have restored the wild-type function at the rII locus.
Determine the values: The number of plaques (areas of phage growth) on E. coli B represents the total number of phages, while the number of plaques on E. coli K12 represents the number of recombinant phages.
Conclude which value is greater: The number of plaques on E. coli B is always greater than or equal to the number of plaques on E. coli K12, as E. coli B supports the growth of both recombinant and non-recombinant phages.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Recombination in Genetics
Recombination is a genetic process where genetic material is exchanged between different chromosomes or within the same chromosome. In the context of phage T4, recombination studies help understand how genetic variation occurs and how traits are inherited. This process is crucial for mapping genetic loci, such as the rII locus, and determining the genetic distance between them.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Recombination after Double Strand Breaks
Phage Growth in Bacterial Strains
Phage growth refers to the replication and proliferation of bacteriophages, which are viruses that infect bacteria. In this study, the growth of phage T4 in different strains of E. coli (K12 and B) is analyzed to assess the efficiency of infection and recombination. The comparison of phage growth in these strains provides insights into the genetic compatibility and the effects of host factors on phage replication.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Conjugation Overview
Simultaneous Infection and Its Implications
Simultaneous infection occurs when multiple phages infect a single bacterial cell at the same time. This method is significant in recombination studies as it allows researchers to observe the interactions between different phage genotypes and their potential to recombine. Typically, the value representing phage growth in the K12 strain is greater than that in the B strain, indicating a higher efficiency of recombination or infection in the K12 background.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Plaques and Experiments

 3:44m
3:44mWatch next
Master Plaques and Experiments with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice