Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
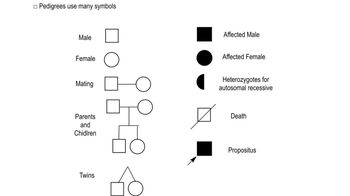
Pedigrees
Problem 1a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn this chapter, we focused on the Mendelian postulates, probability, and pedigree analysis. We also considered some of the methods and reasoning by which these ideas, concepts, and techniques were developed. On the basis of these discussions, what answers would you propose to the following questions: How do we know whether an organism expressing a dominant trait is homozygous or heterozygous?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian genetics is the study of how traits are inherited through generations, based on the principles established by Gregor Mendel. It includes concepts such as dominant and recessive alleles, where dominant traits are expressed in the phenotype even if only one copy of the allele is present. Understanding these principles is crucial for determining the genetic makeup of organisms exhibiting dominant traits.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Descriptive Genetics
Homozygosity vs. Heterozygosity
Homozygosity refers to having two identical alleles for a particular gene, while heterozygosity means having two different alleles. When an organism expresses a dominant trait, it could be either homozygous dominant (two dominant alleles) or heterozygous (one dominant and one recessive allele). Distinguishing between these two states is essential for predicting inheritance patterns in offspring.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Traditional vs. Next-Gen
Test Cross
A test cross is a breeding experiment used to determine the genotype of an organism expressing a dominant trait. By crossing the organism with a homozygous recessive individual, the offspring's phenotypes can reveal whether the dominant organism is homozygous or heterozygous. The ratio of dominant to recessive offspring provides insight into the genetic composition of the parent organism.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Trihybrid Cross

 2:48m
2:48mWatch next
Master Pedigree Symbols with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning