Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
Bacterial Transformation
Problem 10
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDescribe the role of heteroduplex formation during transformation.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Heteroduplex Formation
Heteroduplex formation occurs when two strands of DNA from different sources pair together, resulting in a hybrid molecule. This process is crucial during genetic transformation, where foreign DNA is introduced into a host cell. The heteroduplex can contain mismatches if the sequences are not perfectly complementary, which can lead to genetic variation and evolution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Formation of Plant Gametes
Transformation
Transformation is a process by which a cell takes up foreign DNA from its environment and incorporates it into its own genome. This mechanism is a key method of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria, allowing for genetic diversity and adaptation. The successful integration of the foreign DNA often relies on the formation of heteroduplexes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Transformation
Genetic Recombination
Genetic recombination is the process by which genetic material is rearranged during cell division or through mechanisms like transformation. It can lead to new combinations of alleles, contributing to genetic diversity within a population. Heteroduplexes formed during transformation can undergo repair processes that resolve mismatches, further facilitating recombination and the potential expression of new traits.
Recommended video:
Guided course
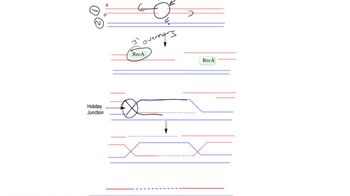
Recombination after Double Strand Breaks

 5:53m
5:53mWatch next
Master Transformation with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

