Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transcription Regulation
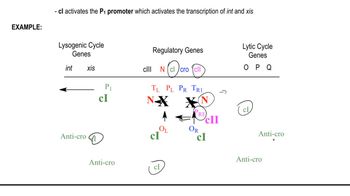
Transcription regulation refers to the mechanisms that control the rate of gene expression by influencing the transcription of DNA into RNA. In the context of phage λ, transcription from the promoter is crucial for determining whether the phage enters a lytic or lysogenic cycle. Mutations that alter transcription levels can significantly impact the expression of genes responsible for these life cycles.
Recommended video:
Lytic vs. Lysogenic Cycle
The lytic cycle is a viral reproductive process that results in the destruction of the host cell, while the lysogenic cycle involves the integration of viral DNA into the host genome, allowing the virus to replicate without killing the host. The decision between these two pathways is influenced by environmental conditions and the levels of specific regulatory proteins, which are affected by transcription levels.
Recommended video:
Decision Between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles
Mutations and Their Effects
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can alter gene function and expression. In this scenario, Mutant 1, which decreases transcription, may favor the lysogenic cycle by reducing the expression of lytic genes, while Mutant 2, which increases transcription, could push the phage towards the lytic cycle by enhancing the expression of genes that promote viral replication and cell lysis.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 4:29m
4:29m