Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
9. Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis
Problem 3
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionWhat role do the following cellular components play in the storage, expression, or transmission of genetic information: (a) chromatin, (b) nucleolus, (c) ribosome, (d) mitochondrion, (e) centriole, (f) centromere?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and proteins found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role in packaging DNA into a compact, dense shape, allowing for efficient storage and regulation of gene expression. Chromatin can exist in two forms: euchromatin, which is less condensed and actively involved in transcription, and heterochromatin, which is more tightly packed and generally inactive.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chromatin
Ribosome
Ribosomes are cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis, translating messenger RNA (mRNA) into polypeptide chains. They can be found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, forming rough ER. Ribosomes facilitate the decoding of genetic information carried by mRNA, linking amino acids together in the order specified by the genetic code, thus playing a vital role in gene expression.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ribosome Structure
Centromere
The centromere is a region of a chromosome that links sister chromatids and is essential during cell division. It serves as the attachment point for spindle fibers, which pull the chromatids apart to ensure proper segregation into daughter cells. The centromere plays a critical role in the transmission of genetic information during mitosis and meiosis, maintaining genetic stability across generations.
Recommended video:
Guided course
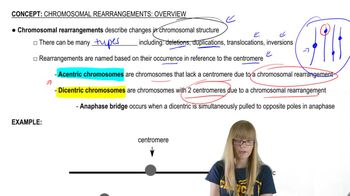
Rearrangement Overview
Related Videos
Related Practice