Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination
DNA Repair
Problem 22e
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDescribe the 'end-replication problem' in eukaryotes. How is it resolved?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
End-Replication Problem
The end-replication problem refers to the difficulty eukaryotic cells face in fully replicating the ends of linear chromosomes during DNA replication. DNA polymerases can only synthesize DNA in one direction and require a primer, which means that the very end of the chromosome cannot be completely copied, leading to progressive shortening of the DNA with each cell division.
Recommended video:
Guided course
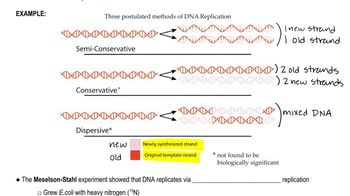
Semiconservative Replication
Telomeres
Telomeres are repetitive nucleotide sequences located at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes that protect them from degradation and prevent the loss of essential genetic information during replication. They act as a buffer zone, ensuring that the coding regions of the DNA are not affected by the end-replication problem, thus maintaining genomic stability.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Telomeres and Telomerase
Telomerase
Telomerase is an enzyme that adds repetitive nucleotide sequences to the telomeres, counteracting the end-replication problem. It is particularly active in stem cells and germ cells, allowing these cells to maintain their telomere length and continue dividing without losing vital genetic information, thus playing a crucial role in cellular aging and cancer biology.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Telomeres and Telomerase

 1:45m
1:45mWatch next
Master DNA Proofreading with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning




