Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
Lambda Bacteriophage and Life Cycle Regulation
Problem 28a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionHow would mutations that inactivate each of the following genes affect the determination of the lytic or lysogenic life cycle in mutated λ phage strains? Explain your answers. N
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles
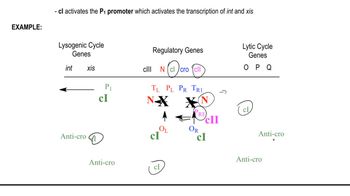
The lytic and lysogenic cycles are two distinct pathways that bacteriophages, like λ phage, can follow after infecting a bacterial host. In the lytic cycle, the phage replicates rapidly, leading to the destruction of the host cell and the release of new phage particles. In contrast, the lysogenic cycle involves the integration of the phage DNA into the host genome, allowing it to replicate along with the host cell without causing immediate harm.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Decision Between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles
Gene Function in Phage Life Cycles
Specific genes in λ phage are crucial for determining whether the phage enters the lytic or lysogenic cycle. For instance, genes like cI and cro play pivotal roles in regulating the switch between these cycles. The cI gene promotes lysogeny by encoding a repressor protein that inhibits lytic gene expression, while the cro gene favors the lytic cycle by repressing lysogenic genes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bacteriophage Life Cycle
Mutations and Their Effects
Mutations that inactivate genes involved in the lytic or lysogenic cycles can significantly alter the behavior of λ phage. For example, a mutation in the cI gene may prevent the establishment of lysogeny, leading to a predominance of the lytic cycle, while a mutation in the cro gene could result in a failure to initiate the lytic cycle, favoring lysogeny instead. Understanding these mutations helps elucidate the genetic control of phage life cycles.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Maternal Effect

 4:29m
4:29mWatch next
Master Bacteriophage Life Cycle with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning

