Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
9. Mitosis and Meiosis
Meiosis
Problem 31
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionA species of cereal rye (Secale cereale) has a chromosome number of 14, while a species of Canadian wild rye (Elymus canadensis) has a chromosome number of 28. Sterile hybrids can be produced by crossing Secale with Elymus. Given that none of the chromosomes pair at meiosis I in the sterile hybrid (Hang and Franckowlak, 1984), speculate on the anaphase I separation patterns of these chromosomes.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
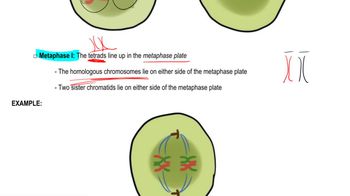
Chromosome Number and Meiosis
Chromosome number refers to the total number of chromosomes in a cell. In meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and segregate into daughter cells. In the case of the sterile hybrid between Secale cereale (14 chromosomes) and Elymus canadensis (28 chromosomes), the mismatch in chromosome numbers leads to difficulties in pairing during meiosis, resulting in no homologous chromosomes aligning at meiosis I.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Meiosis Overview
Hybrid Sterility
Hybrid sterility occurs when the offspring of two different species are unable to reproduce. In this case, the hybrid between Secale and Elymus is sterile because the differing chromosome numbers prevent proper pairing and segregation during meiosis, leading to gametes that lack the necessary genetic material for successful reproduction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Drosophila P Element
Anaphase I and Chromosome Separation
Anaphase I is the stage of meiosis where homologous chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite poles of the cell. In the sterile hybrid, since no chromosomes pair during meiosis I, the separation pattern would involve random movement of unpaired chromosomes, leading to an unequal distribution and potentially resulting in gametes with varying and incomplete sets of chromosomes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chromosome Structure

 5:30m
5:30mWatch next
Master Meiosis Overview with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice