Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
7. DNA and Chromosome Structure
DNA Structure
Problem 12a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionHuman adult hemoglobin is a tetramer containing two alpha (α) and two beta (β) polypeptide chains. The α gene cluster on chromosome 16 and the β gene cluster on chromosome 11 share amino acid similarities such that 61 of the amino acids of the α-globin polypeptide (141 amino acids long) are shared in identical sequence with the β-globin polypeptide (146 amino acids long). How might one explain the existence of two polypeptides with partially shared function and structure on two different chromosomes?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gene Duplication
Gene duplication is a process where a segment of DNA is copied, resulting in two identical or similar genes. This can lead to the evolution of new functions as one gene may retain the original function while the other accumulates mutations over time. In the case of hemoglobin, the α and β globin genes likely arose from a common ancestral gene through duplication, allowing for specialization in function while maintaining some structural similarities.
Recommended video:
Guided course
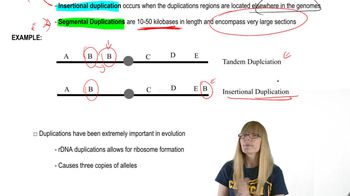
Duplications
Chromosomal Location and Evolution
The location of genes on different chromosomes can influence their evolutionary paths. Genes that are located on separate chromosomes, like the α and β globin genes, can evolve independently, allowing for variations in expression and function. This separation can lead to the development of distinct polypeptides that still share functional roles, as seen in the cooperative binding of oxygen by hemoglobin.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Evolution
Functional Redundancy
Functional redundancy refers to the phenomenon where different genes or proteins can perform similar functions within a biological system. In the case of hemoglobin, the α and β chains exhibit functional redundancy in oxygen transport, allowing for a robust system that can adapt to varying physiological conditions. This redundancy can be advantageous, as it provides a backup mechanism if one polypeptide is mutated or not expressed.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Functional Genomics
Related Videos
Related Practice




