Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
Lac Operon
Problem 1e
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIn this chapter, we focused on the regulation of gene expression in bacteria. Along the way, we found many opportunities to consider the methods and reasoning by which much of this information was acquired. From the explanations given in the chapter, what answers would you propose to the following fundamental questions? What led researchers to conclude that a repressor molecule regulates the lac operon?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
26sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
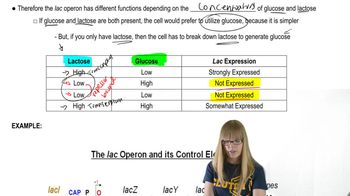
Lac Operon
The lac operon is a set of genes in bacteria, specifically E. coli, that are involved in the metabolism of lactose. It consists of structural genes that encode proteins necessary for lactose uptake and breakdown, and it is regulated by a promoter and an operator. Understanding the lac operon is crucial for grasping how bacteria adapt to different energy sources and how gene expression is controlled in response to environmental changes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lac Operon Overview
Repressor Molecule
A repressor molecule is a type of protein that binds to specific DNA sequences, inhibiting the transcription of certain genes. In the context of the lac operon, the lac repressor binds to the operator region, preventing RNA polymerase from transcribing the downstream genes when lactose is absent. This mechanism is a key example of negative regulation in gene expression, demonstrating how cells conserve resources by only expressing genes when their products are needed.
Recommended video:
Guided course
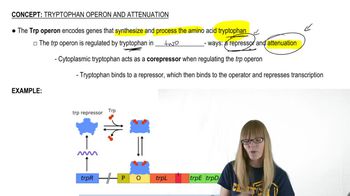
Trp Repressor
Gene Regulation Mechanisms
Gene regulation mechanisms are processes that control the timing and amount of gene expression in response to internal and external signals. In bacteria, these mechanisms include operons, repressors, and activators, which work together to ensure that genes are expressed only when necessary. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for interpreting experimental results and the conclusions drawn about how specific molecules, like repressors, influence gene expression.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Review of Regulation

 4:27m
4:27mWatch next
Master Lac Operon Overview with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning