Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance
Chi Square Analysis
Problem 30a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDr. Ara B. Dopsis and Dr. C. Ellie Gans are performing genetic crosses on daisy plants. They self-fertilize a blue-flowered daisy and grow 100 progeny plants that consist of 55 blue-flowered plants, 22 purple-flowered plants, and 23 white-flowered plants. Dr. Dopsis believes this is the result of segregation of two alleles at one locus and that the progeny ratio is 1:2:1. Dr. Gans thinks the progeny phenotypes are the result of two epistatic genes and that the ratio is 9:3:4.
The two scientists ask you to resolve their conflict by performing chi-square analysis on the data for both proposed genetic mechanisms. For each proposed mechanism, fill in the values requested on the form the researchers have provided for your analysis.
Using any of the 100 progeny plants, propose a cross that will verify the conclusion you proposed in part (c). Plants may be self-fertilized, or one plant can be crossed to another. What result will be consistent with the 1:2:1 hypothesis? What result will be consistent with the 9:3:4 hypothesis?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian genetics is the study of how traits are inherited through the segregation and independent assortment of alleles. Gregor Mendel's principles, particularly the law of segregation, explain how alleles for a trait separate during gamete formation, leading to predictable ratios in offspring. In this case, the 1:2:1 ratio proposed by Dr. Dopsis suggests a single gene with two alleles, where homozygous individuals produce one type of gamete, while heterozygous individuals produce two types.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Descriptive Genetics
Epistasis
Epistasis refers to the interaction between genes, where the expression of one gene can mask or modify the expression of another gene. This phenomenon can lead to non-Mendelian ratios in offspring, such as the 9:3:4 ratio suggested by Dr. Gans. In this scenario, two genes may control flower color, with one gene's dominant allele suppressing the expression of another gene's alleles, resulting in a modified phenotypic ratio.
Recommended video:
Guided course
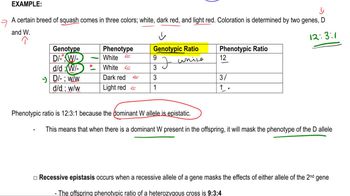
Epistatic Genes
Chi-Square Analysis
Chi-square analysis is a statistical method used to determine if there is a significant difference between observed and expected frequencies in categorical data. In the context of genetics, it helps assess whether the observed progeny ratios fit the expected ratios based on proposed inheritance models. By calculating the chi-square value and comparing it to a critical value from the chi-square distribution, researchers can evaluate the validity of the genetic hypotheses presented by Dr. Dopsis and Dr. Gans.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square Analysis

 2:48m
2:48mWatch next
Master Chi Square Analysis with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice








