Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Probability and Genetics
Problem 19c
Textbook Question
If two six-sided dice are rolled, what is the probability that the total number of spots showing is
7?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
<span>Step 1: Understand the problem. We need to find the probability that the sum of the numbers on two six-sided dice equals 7.</span>
<span>Step 2: Determine the total number of possible outcomes when rolling two dice. Since each die has 6 sides, the total number of outcomes is 6 \times 6 = 36.</span>
<span>Step 3: Identify the successful outcomes where the sum of the numbers on the two dice equals 7. These pairs are (1,6), (2,5), (3,4), (4,3), (5,2), and (6,1).</span>
<span>Step 4: Count the number of successful outcomes. There are 6 pairs that result in a sum of 7.</span>
<span>Step 5: Calculate the probability by dividing the number of successful outcomes by the total number of possible outcomes: \frac{6}{36}.</span>
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Probability
Probability is a measure of the likelihood that a particular event will occur, expressed as a ratio of favorable outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes. In the context of rolling dice, it quantifies how often a specific total, such as 7, can be achieved compared to all possible outcomes when two dice are rolled.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Probability
Sample Space
The sample space is the set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment. For rolling two six-sided dice, the sample space consists of 36 combinations (6 sides on the first die multiplied by 6 sides on the second die), which helps in calculating the probability of specific outcomes like rolling a total of 7.
Recommended video:
Guided course
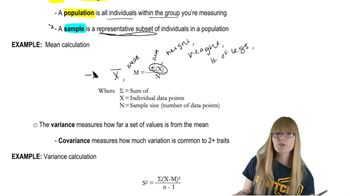
Mathematical Measurements
Favorable Outcomes
Favorable outcomes refer to the specific results that satisfy the condition of the probability question. In this case, the favorable outcomes for rolling a total of 7 with two dice include the combinations (1,6), (2,5), (3,4), (4,3), (5,2), and (6,1), totaling six combinations that contribute to the desired outcome.
Recommended video:
Guided course
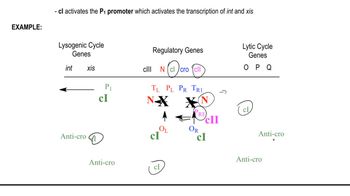
Decision Between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles
Related Videos
Related Practice



