Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
Lac Operon
Problem 15
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionThe creation of milk products such as cheeses and yogurts is dependent on the conversion by various anaerobic bacteria, including several Lactobacillus species, of lactose to glucose and galactose, ultimately producing lactic acid. These conversions are dependent on both permease and β-galactosidase as part of the lac operon. After selection for rapid fermentation for the production of yogurt, one Lactobacillus subspecies lost its ability to regulate lac operon expression [Lapierre, L., et al. (2002). J. Bacteriol. 184:928–935]. Would you consider it likely that in this subspecies the lac operon is on or off? What genetic events would likely contribute to the loss of regulation as described above?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lac Operon
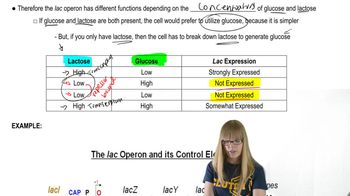
The lac operon is a set of genes in bacteria that are involved in the metabolism of lactose. It includes genes for β-galactosidase, which breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose, and permease, which facilitates lactose entry into the cell. The operon is regulated by the presence or absence of lactose, allowing bacteria to efficiently use lactose as an energy source when available.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lac Operon Overview
Gene Regulation
Gene regulation refers to the mechanisms that control the expression of genes, determining when and how much of a gene product is made. In the context of the lac operon, regulation is achieved through the binding of repressor proteins and the presence of inducers like lactose, which can activate or deactivate the operon. Loss of regulation can lead to continuous expression of the operon, regardless of lactose availability.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Review of Regulation
Mutations and Genetic Events
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can affect gene function and regulation. In the case of the Lactobacillus subspecies, genetic events such as point mutations, deletions, or insertions in the regulatory regions of the lac operon could lead to a loss of regulation. These mutations may result in the operon being constitutively active (always 'on') or inactive, impacting the organism's ability to metabolize lactose effectively.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mutations and Phenotypes

 4:27m
4:27mWatch next
Master Lac Operon Overview with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning