Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance
Chi Square Analysis
Problem 33
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDr. O. Sophila, a close friend of Dr. Ara B. Dopsis, reviews the results Dr. Dopsis obtained in his experiment with iris plants described in Genetic Analysis 4.3. Dr. Sophila thinks the F₂ progeny demonstrate that a single gene with incomplete dominance has produced a 1:2:1 ratio. Dr. Dopsis insists his proposal of recessive epistasis producing a 9:4:3 ratio in the F₂ is correct. To test his proposal, Dr. Dopsis examines the F₂ data under the assumptions of the single-gene incomplete dominance model using chi-square analysis. Calculate and interpret this chi-square value. Can Dr. Dopsis reject the single-gene incomplete dominance model on the basis of this analysis? Explain why or why not.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Incomplete Dominance
Incomplete dominance is a genetic phenomenon where the phenotype of heterozygotes is intermediate between those of the two homozygotes. This results in a blending of traits, leading to a 1:2:1 phenotypic ratio in the offspring when two heterozygous individuals are crossed. For example, in flower color, a red flower crossed with a white flower may produce pink flowers in the F1 generation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Variations on Dominance
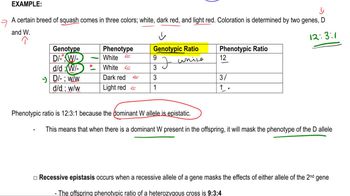
Recessive Epistasis
Recessive epistasis occurs when the presence of two recessive alleles at one gene locus masks the expression of alleles at another locus. This can lead to a modified phenotypic ratio, such as 9:4:3, in the offspring. In the context of the iris plants, this means that certain combinations of alleles can prevent the expression of other traits, altering expected ratios from simple Mendelian inheritance.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Epistatic Genes
Chi-Square Analysis
Chi-square analysis is a statistical method used to determine if there is a significant difference between observed and expected frequencies in categorical data. In genetics, it helps assess whether the observed ratios of phenotypes fit a specific inheritance model. A high chi-square value indicates a poor fit to the model, allowing researchers to reject or accept hypotheses about genetic inheritance patterns.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square Analysis

 2:48m
2:48mWatch next
Master Chi Square Analysis with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice








