Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
15. Genomes and Genomics
Functional Genomics
Problem 20b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionSubstantial fractions of the genomes of many plants consist of segmental duplications; for example, approximately 40% of genes in the Arabidopsis genome are duplicated. How might you approach the functional characterization of such genes using reverse genetics?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Segmental Duplications
Segmental duplications refer to large regions of the genome that have been duplicated and can lead to gene redundancy. In plants like Arabidopsis, these duplications can significantly impact genetic diversity and evolution. Understanding these duplications is crucial for functional studies, as they can complicate the interpretation of gene function due to the presence of multiple similar genes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
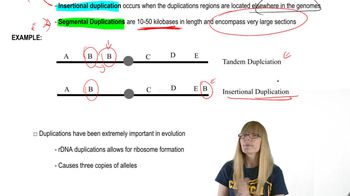
Duplications
Reverse Genetics
Reverse genetics is a method used to understand the function of a gene by analyzing the phenotypic effects of specific gene modifications. This approach often involves techniques such as gene knockout, where a gene is deliberately disrupted to observe changes in the organism. In the context of segmental duplications, reverse genetics can help determine which duplicated gene is responsible for a particular trait or function.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Genetic Cloning
Functional Characterization
Functional characterization involves determining the role and activity of a gene within an organism. This process typically includes assessing gene expression patterns, protein interactions, and phenotypic outcomes of gene modifications. For duplicated genes, functional characterization is essential to discern the unique contributions of each gene copy, especially when they may have redundant or divergent functions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Functional Genomics

 8:26m
8:26mWatch next
Master Functional Genomics with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice

