Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Nucleotides
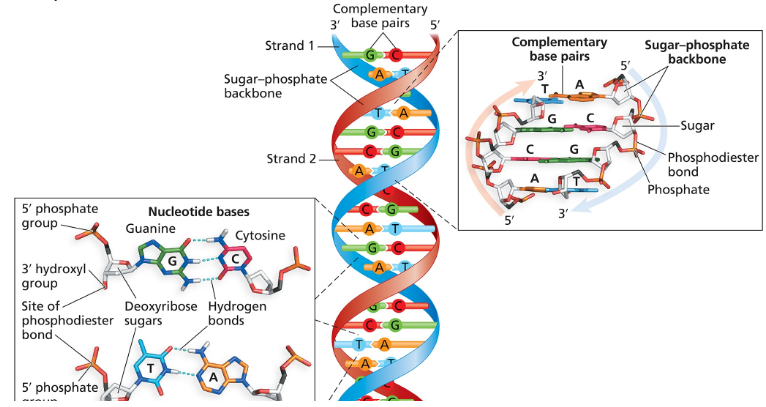
Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and RNA, consisting of three components: a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. In DNA, the sequence of these nucleotides encodes genetic information. Understanding the structure of nucleotides is essential for analyzing DNA sequences and their complementary pairs.
Recommended video:
Complementary Base Pairing
Complementary base pairing refers to the specific pairing of nitrogenous bases in DNA, where adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). This pairing is crucial for the formation of the double helix structure of DNA and ensures accurate replication and transcription of genetic information. Recognizing these pairs is vital for determining the complementary sequence of a given DNA strand.
Recommended video:
Phosphodiester Bonds
Phosphodiester bonds are covalent bonds that link nucleotides together in a DNA or RNA strand. They form between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group of the sugar of another, creating a sugar-phosphate backbone. The number of phosphodiester bonds in a DNA duplex can be calculated by counting the number of nucleotides in the strand and subtracting one, as each bond connects two nucleotides.
Recommended video:
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:

