Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Meiosis and Chromosome Segregation
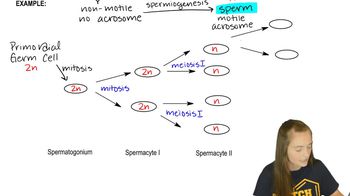
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four haploid cells. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes are separated, while meiosis II separates sister chromatids. Errors in this process, such as premature centromere division, can lead to aneuploidy, where gametes have an abnormal number of chromosomes.
Recommended video:
Chromosome 21 and Down Syndrome
Chromosome 21 is one of the smallest human chromosomes and is associated with Down syndrome when there is an extra copy (trisomy 21). If a secondary oocyte has a single chromatid for chromosome 21, it indicates that one homologous chromosome was not properly segregated. If this oocyte is fertilized, it could lead to an embryo with an abnormal number of chromosome 21, potentially resulting in Down syndrome.
Recommended video:
Polar Bodies and Oocyte Development
During oocyte development, polar bodies are small cells that are produced alongside the oocyte during meiosis but typically do not develop into ova. The first polar body contains the genetic material that was not included in the secondary oocyte. The presence of a single chromatid in the first polar body suggests that the secondary oocyte may have an abnormal chromosomal complement, which can affect fertilization outcomes.
Recommended video:
 Verified Solution
Verified Solution


 21:21m
21:21m
