Researchers examined a family with an interesting distribution of Leigh syndrome symptoms. In this disorder, individuals may show a progressive loss of motor function (ataxia, A) with peripheral neuropathy (PN, meaning impairment of the peripheral nerves). A mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutation that reduces ATPase activity was identified in various tissues of affected individuals. The accompanying table summarizes the presence of symptoms in an extended family.
Person Condition Percent Mitochondria with
Mutation
Proband A and PN >90%
Brother A and PN >90%
Brother Asymptomatic 17%
Mother PN 86%
Maternal uncle PN 85%
Maternal cousin A and PN 90%
Maternal cousin A and PN 91%
Maternal Asymptomatic 56%
grandmother
How can some individuals in the same family show such variation in symptoms? What term, as related to organelle heredity, describes such variation?
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Pedigrees
Problem 20b
Textbook Question
For each pedigree shown,
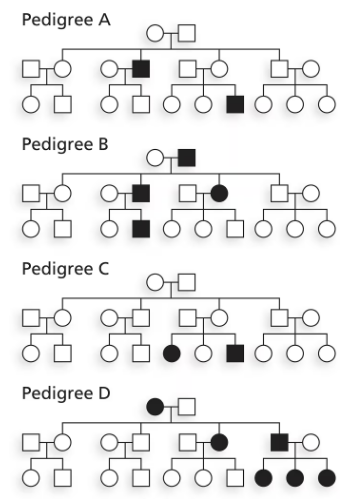
Determine which other pattern(s) of transmission is/are possible. For each possible mode of transmission, specify the genotypes necessary for transmission to occur.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Examine the pedigree carefully to identify the pattern of inheritance. Look for clues such as whether the trait appears in every generation (dominant) or skips generations (recessive), and whether it affects males and females equally (autosomal) or disproportionately affects one sex (sex-linked).
Consider autosomal dominant inheritance: If the trait is dominant, individuals with the trait must have at least one dominant allele. Determine the genotypes of affected individuals (e.g., heterozygous Aa or homozygous AA) and unaffected individuals (e.g., homozygous recessive aa).
Consider autosomal recessive inheritance: If the trait is recessive, affected individuals must have two recessive alleles (aa). Unaffected individuals could be carriers (Aa) or homozygous dominant (AA). Check if the pattern fits this mode of inheritance.
Consider X-linked inheritance: If the trait is X-linked, analyze whether males (XY) and females (XX) are affected differently. For X-linked recessive traits, affected males must inherit the recessive allele from their mother, while affected females must inherit two recessive alleles. For X-linked dominant traits, affected males pass the trait to all daughters but not sons.
Summarize the possible modes of transmission and specify the genotypes required for each mode. For example, autosomal dominant requires Aa or AA for affected individuals, autosomal recessive requires aa, and X-linked inheritance requires specific combinations of alleles on the X chromosome.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Pedigree Analysis
Pedigree analysis is a diagrammatic method used to trace the inheritance of traits through generations in a family. It helps identify patterns of inheritance, such as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, and X-linked recessive traits. By analyzing the pedigree, one can determine the likelihood of certain genotypes appearing in offspring based on the genotypes of the parents.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Pedigree Flowchart
Modes of Inheritance
Modes of inheritance refer to the patterns through which genetic traits are passed from parents to offspring. The primary modes include autosomal dominant, where only one copy of a mutated gene is sufficient for expression, and autosomal recessive, where two copies are needed. Understanding these modes is crucial for predicting the genotypes of individuals in a pedigree and determining the likelihood of trait transmission.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Organelle Inheritance
Genotype Specification
Genotype specification involves identifying the specific alleles present in an individual that contribute to a particular trait. In the context of pedigrees, it is essential to determine the genotypes of individuals to understand how traits are inherited. This includes recognizing homozygous and heterozygous conditions, which influence the expression of dominant and recessive traits in offspring.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Gamete Genotypes
Related Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
408
views


