Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
6. Chromosomal Variation
Chromosomal Rearrangements: Duplications
Problem 13
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDiscuss Ohno's hypothesis on the role of gene duplication in the process of evolution. What evidence supports this hypothesis?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gene Duplication
Gene duplication is a process where a segment of DNA is copied, resulting in two identical or similar genes. This can lead to genetic redundancy, allowing one copy to maintain its original function while the other can evolve new functions. This mechanism is a significant source of genetic variation and is crucial for the evolution of new traits and functions in organisms.
Recommended video:
Guided course
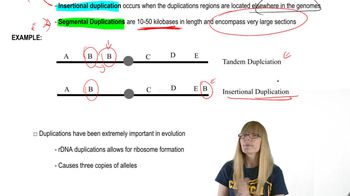
Duplications
Ohno's Hypothesis
Ohno's hypothesis, proposed by Susumu Ohno in the 1960s, suggests that gene duplication is a major driving force in evolution. According to this hypothesis, duplicated genes can diverge over time, leading to the development of new functions and complexity in organisms. This idea emphasizes the importance of gene duplication in creating genetic diversity and facilitating evolutionary innovation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
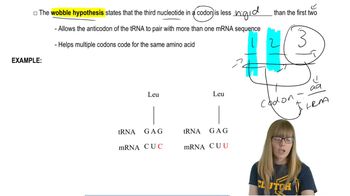
Translation:Wobble Hypothesis
Evidence Supporting Gene Duplication
Evidence supporting Ohno's hypothesis includes comparative genomic studies that show conserved gene families across different species, indicating common ancestry through duplication events. Additionally, experimental studies have demonstrated that duplicated genes can acquire new functions through mutations, leading to phenotypic diversity. The presence of pseudogenes, which are non-functional remnants of duplicated genes, also supports the idea that gene duplication is a common evolutionary mechanism.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Duplications
Related Videos
Related Practice



