Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
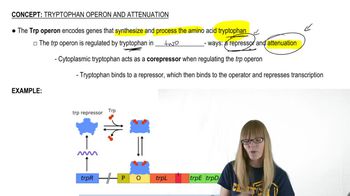
Tryptophan Operon and Attenuation
Problem 24b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionFigure 16.13 depicts numerous critical regions of the leader sequence of mRNA that play important roles during the process of attenuation in the trp operon. A closer view of the leader sequence, which begins at about position 30 downstream from the 5' end, is shown below, running along both columns. Within this molecule are the sequences that cause the formation of the alternative hairpins. It also contains the successive triplets that encode tryptophan, where stalling during translation occurs. Take a large piece of paper (such as manila wrapping paper) and, along with several other students from your genetics class, work through the base sequence to identify the trp codons and the parts of the molecule representing the base-pairing regions that form the terminator and antiterminator hairpins shown in Figure 16.13.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
35sPlay a video:
275
views
Was this helpful?
Video transcript
Related Videos
Related Practice