Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
16. Transposable Elements
Discovery of Transposable Elements
Problem 17
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDescribe the difference between DNA transposons and retrotransposons.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
DNA Transposons
DNA transposons, also known as 'jumping genes,' are segments of DNA that can move from one location to another within the genome. They typically replicate themselves and insert copies into new genomic sites, a process facilitated by the enzyme transposase. This movement can lead to mutations and genomic rearrangements, influencing gene expression and evolution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

DNA Proofreading
Retrotransposons
Retrotransposons are a type of transposable element that move within the genome via an RNA intermediate. They are transcribed into RNA, which is then reverse-transcribed back into DNA and integrated into a new location in the genome. This process often involves the enzyme reverse transcriptase and can contribute to genetic diversity and evolution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Eukaryotic Transposable Elements
Mechanisms of Transposition
The mechanisms of transposition differ between DNA transposons and retrotransposons. DNA transposons utilize a 'cut-and-paste' mechanism, while retrotransposons employ a 'copy-and-paste' strategy. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial for grasping how these elements can affect genomic stability, gene regulation, and evolutionary processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
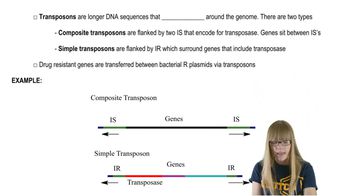
Prokaryotic Transposable Elements
Related Videos
Related Practice




