Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
9. Mitosis and Meiosis
Meiosis
Problem 2a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionWrite a short essay that contrasts mitosis and meiosis, including their respective roles in organisms, the mechanisms by which they achieve their respective outcomes, and the consequences should either process fail to be executed with absolute fidelity.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
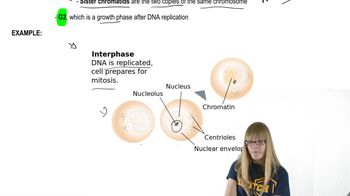
Mitosis
Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It plays a crucial role in growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in organisms. The process involves several stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, ensuring accurate duplication and distribution of genetic material.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Mitosis Steps
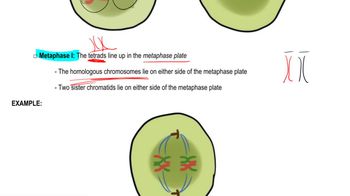
Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically diverse gametes. This process is essential for sexual reproduction, as it introduces genetic variation through independent assortment and crossing over. Meiosis consists of two rounds of division: meiosis I and meiosis II, each with distinct phases that contribute to genetic diversity.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Meiosis Overview
Consequences of Division Errors
Errors in mitosis or meiosis can lead to significant consequences, such as cancer or genetic disorders. In mitosis, improper chromosome segregation can result in aneuploidy, where cells have an abnormal number of chromosomes. In meiosis, errors can lead to conditions like Down syndrome, caused by an extra chromosome 21, highlighting the importance of fidelity in these processes for organismal health.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Proofreading

 5:30m
5:30mWatch next
Master Meiosis Overview with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice