Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
16. Transposable Elements
Transposable Elements in Eukaryotes
Problem 22
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIt is estimated that about 0.2 percent of human mutations are due to TE insertions, and a much higher degree of mutational damage is known to occur in some other organisms. In what way might a TE insertion contribute positively to evolution?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Transposable Elements (TEs)
Transposable elements, or TEs, are DNA sequences that can change their position within the genome. They can cause mutations by inserting themselves into or near genes, potentially disrupting normal gene function. However, TEs can also create genetic diversity, which is a key driver of evolution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
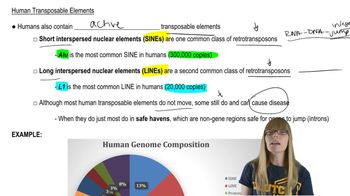
Human Transposable Elements
Mutational Effects
Mutations can have various effects on an organism, ranging from neutral to beneficial or harmful. TE insertions can lead to new gene functions or regulatory changes, which may enhance an organism's adaptability to its environment. This process can contribute to evolutionary innovation by providing raw material for natural selection.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Maternal Effect
Evolutionary Adaptation
Evolutionary adaptation refers to the process by which a species becomes better suited to its environment through genetic changes. TE insertions can introduce new traits that may confer advantages, such as increased resistance to diseases or improved metabolic functions, thereby facilitating the survival and reproduction of organisms in changing environments.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Overview

 3:21m
3:21mWatch next
Master Eukaryotic Transposable Elements with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning


