Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance
Variations of Dominance
Problem 8b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionTwo genes interact to produce various phenotypic ratios among F₂ progeny of a dihybrid cross. Design a different pathway explaining each of the F₂ ratios below, using hypothetical genes R and T and assuming that the dominant allele at each locus catalyzes a different reaction or performs an action leading to pigment production. The recessive allele at each locus is null (loss-of-function). Begin each pathway with a colorless precursor that produces a white or albino phenotype if it is unmodified. The ratios are for F₂ progeny produced by crossing wild-type F₁ organisms with the genotype RrTt.
9/16 black : 3/16 gray : 4/16 albino
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dihybrid Cross
A dihybrid cross involves two traits, each controlled by different genes, typically represented by two pairs of alleles. In this case, the genes R and T are being analyzed for their interactions in producing phenotypes. The classic Mendelian ratio for a dihybrid cross of two heterozygous parents (RrTt x RrTt) is 9:3:3:1, but in this scenario, the interaction between the genes modifies the expected ratios, leading to a more complex outcome.
Recommended video:
Guided course
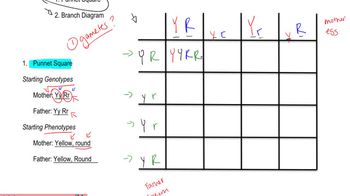
Punnet Square
Epistasis
Epistasis occurs when the expression of one gene is affected by another gene, leading to modified phenotypic ratios. In this question, the dominant alleles of genes R and T interact in such a way that they influence pigment production pathways. Understanding how these genes interact is crucial for explaining the observed ratios of black, gray, and albino phenotypes among the F₂ progeny.
Recommended video:
Guided course
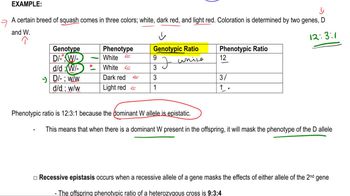
Epistatic Genes
Phenotypic Ratios
Phenotypic ratios represent the relative frequencies of different phenotypes in the offspring resulting from a genetic cross. In this case, the ratios of 9/16 black, 3/16 gray, and 4/16 albino indicate how the interactions between the alleles of genes R and T lead to varying levels of pigment production. Analyzing these ratios helps in constructing the pathways that explain the genetic interactions at play.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mutations and Phenotypes

 4:37m
4:37mWatch next
Master Variations on Dominance with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice


