Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
Bacteriophage Genetics
Problem 22i
Textbook Question
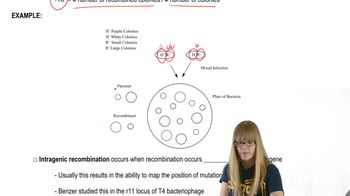
Textbook QuestionIn studies of recombination between mutants 1 and 2 from Problem 21, the results shown in the following table were obtained. Strain Dilution Plaques Phenotypes E. coli B 10⁻⁷ 4 r E. coli K12 10⁻² 8 + Calculate the recombination frequency.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Recombination Frequency
Recombination frequency is a measure of the likelihood that two genes will be separated during meiosis due to crossing over. It is calculated by dividing the number of recombinant offspring by the total number of offspring, often expressed as a percentage. This frequency provides insights into the genetic linkage between genes, with lower frequencies indicating closer linkage.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Recombination after Single Strand Breaks
Genetic Linkage
Genetic linkage refers to the tendency of genes located close to each other on a chromosome to be inherited together during meiosis. Linked genes do not assort independently, which can affect the ratios of phenotypes observed in offspring. Understanding linkage is crucial for interpreting recombination frequencies and mapping genes on chromosomes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square and Linkage
Phenotype and Genotype
Phenotype refers to the observable characteristics or traits of an organism, which result from the interaction of its genotype (the genetic makeup) with the environment. In genetic studies, distinguishing between different phenotypes, such as mutants and wild types, is essential for analyzing inheritance patterns and calculating recombination frequencies.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Gamete Genotypes

 3:44m
3:44mWatch next
Master Plaques and Experiments with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice