Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
9. Mitosis and Meiosis
Meiosis
Problem 10
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionDefine and discuss these terms: (a) synapsis, (b) bivalents, (c) chiasmata, (d) crossing over, (e) chromomeres, (f) sister chromatids, (g) tetrads, (h) dyads, (i) monads.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Synapsis
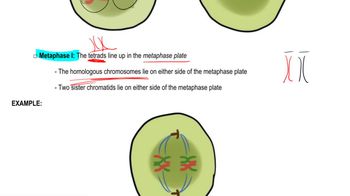
Synapsis is the process during meiosis where homologous chromosomes pair up closely along their lengths. This pairing is crucial for the exchange of genetic material and occurs during prophase I of meiosis. The close alignment allows for the formation of structures called bivalents, which facilitate genetic recombination.
Chiasmata
Chiasmata are the points where homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material during meiosis. They form as a result of crossing over, where segments of DNA are swapped between non-sister chromatids. This process increases genetic diversity in gametes and is visually represented in the image, highlighting the areas where chromosomes are intertwined.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Meiosis Steps
Crossing Over
Crossing over is a genetic recombination process that occurs during prophase I of meiosis, where segments of DNA are exchanged between homologous chromosomes. This exchange results in new combinations of alleles, contributing to genetic variation in offspring. It is a key mechanism for evolution and adaptation in populations.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Discovery of Crossing Over

 5:30m
5:30mWatch next
Master Meiosis Overview with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice


