Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
6. Chromosomal Variation
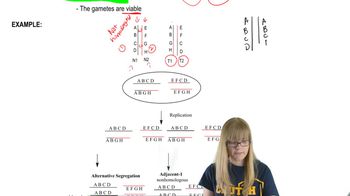
Chromosomal Rearrangements: Translocations
Problem 24c
Textbook Question
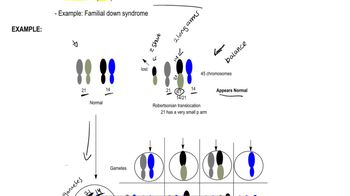
Textbook QuestionA boy with Down syndrome (trisomy 21) has 46 chromosomes. His parents and his two older sisters have a normal phenotype, but each has 45 chromosomes.
How many chromosomes do you expect to see in karyotypes of the parents?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Karyotype
A karyotype is a visual representation of an individual's chromosomes, organized in pairs and arranged by size. It is used to identify chromosomal abnormalities, such as aneuploidies, which involve an abnormal number of chromosomes. In humans, a normal karyotype consists of 46 chromosomes, arranged in 23 pairs.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Human Sex Chromosomes
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy refers to the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell. This can result from nondisjunction during meiosis, where chromosomes fail to separate properly, leading to gametes with too many or too few chromosomes. In the case of Down syndrome, an extra copy of chromosome 21 results in trisomy 21, while the parents in this scenario may exhibit a different chromosomal count.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Aneuploidy
Inheritance Patterns
Inheritance patterns describe how genetic traits and conditions are passed from parents to offspring. In the case of Down syndrome, it is typically not inherited but arises from random errors in cell division. Understanding these patterns helps in predicting the likelihood of genetic conditions based on parental genotypes and karyotypes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Organelle Inheritance

 12:42m
12:42mWatch next
Master Reciprocal Translocation with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice