Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Pedigrees
Problem 15c
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionThe accompanying pedigree shows the transmission of albinism (absence of skin pigment) in a human family.
What is the probability that female I-3 is a heterozygous carrier of the allele for albinism?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
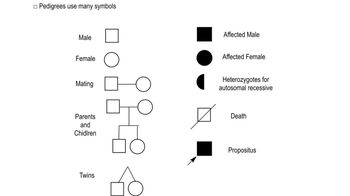
Pedigree Analysis
Pedigree analysis is a diagrammatic method used to trace the inheritance patterns of traits through generations in a family. It helps identify whether a trait is dominant or recessive, and can indicate the genotypes of individuals based on their phenotypes and the phenotypes of their relatives. Understanding how to read and interpret pedigrees is crucial for determining the likelihood of genetic traits being passed on.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Pedigree Flowchart
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
Albinism is typically inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning that an individual must inherit two copies of the recessive allele (one from each parent) to express the trait. Carriers, who have one dominant and one recessive allele, do not show the trait but can pass the recessive allele to their offspring. Recognizing this inheritance pattern is essential for calculating the probability of an individual being a carrier.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Autosomal Pedigrees
Probability in Genetics
Probability in genetics involves calculating the likelihood of certain genotypes or phenotypes occurring in offspring based on parental genotypes. This is often done using tools like Punnett squares or by applying the principles of Mendelian inheritance. In the context of the question, understanding how to assess the probability that female I-3 is a heterozygous carrier requires knowledge of the genotypes of her parents and the inheritance patterns of albinism.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Probability

 2:48m
2:48mWatch next
Master Pedigree Symbols with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning