Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
Probability and Genetics
Problem 19b
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionIf two six-sided dice are rolled, what is the probability that the total number of spots showing is
greater than 5?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
46sPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Probability
Probability is a measure of the likelihood that a particular event will occur, expressed as a number between 0 and 1. In this context, it quantifies the chance of rolling a total greater than 5 with two six-sided dice. Understanding probability involves calculating the ratio of favorable outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Probability
Sample Space
The sample space is the set of all possible outcomes of a random experiment. For rolling two six-sided dice, the sample space consists of 36 outcomes, as each die has 6 faces. Identifying the sample space is crucial for calculating probabilities, as it provides the basis for determining how many outcomes meet the criteria of the event in question.
Recommended video:
Guided course
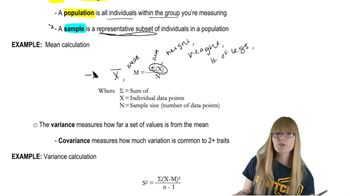
Mathematical Measurements
Favorable Outcomes
Favorable outcomes are the specific results of an experiment that satisfy the conditions of the event being analyzed. In this case, favorable outcomes are the combinations of dice rolls that result in a total greater than 5. Counting these outcomes accurately is essential for calculating the probability of the event.
Recommended video:
Guided course
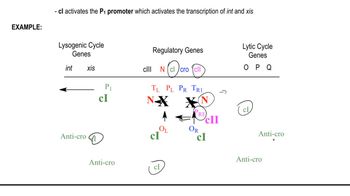
Decision Between Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles
Related Videos
Related Practice



