Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Mapping Genes
Problem 15a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionAnother cross in Drosophila involved the recessive, X-linked genes yellow (y), white (w), and cut (ct). A yellow-bodied, white-eyed female with normal wings was crossed to a male whose eyes and body were normal but whose wings were cut. The F₁ females were wild type for all three traits, while the F₁ males expressed the yellow-body and white-eye traits. The cross was carried to an F₂ progeny, and only male offspring were tallied. On the basis of the data shown here, a genetic map was constructed. Phenotype Male Offspring y + ct 9 + w + 6 y w ct 90 + + + 95 + + ct 424 y w + 376 y + + 0 + w ct 0 Could the F₂ female offspring be used to construct the map? Why or why not?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
X-linked Inheritance
X-linked inheritance refers to the pattern of inheritance for genes located on the X chromosome. In Drosophila, males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome, while females have two X chromosomes. This means that recessive traits linked to the X chromosome will manifest in males if they inherit the recessive allele, while females require two copies of the recessive allele to express the trait. Understanding this concept is crucial for analyzing the inheritance patterns observed in the F₂ generation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

X-Inactivation
Phenotypic Ratios
Phenotypic ratios are the relative frequencies of different phenotypes in the offspring resulting from a genetic cross. In this case, the observed ratios of male offspring phenotypes provide insights into the linkage and recombination frequencies of the genes involved. By analyzing these ratios, one can infer the genetic relationships between traits and construct a genetic map. This concept is essential for interpreting the data from the F₂ progeny and understanding the inheritance patterns.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mutations and Phenotypes
Genetic Mapping
Genetic mapping is the process of determining the relative positions of genes on a chromosome based on recombination frequencies. It involves analyzing the offspring's phenotypes to estimate the distances between genes, with closer genes having lower recombination rates. In this scenario, the F₂ male offspring data is used to construct a genetic map, but the F₂ female offspring cannot be used effectively due to their potential to mask the expression of X-linked traits. Understanding genetic mapping is vital for interpreting the results of the cross.
Recommended video:
Guided course
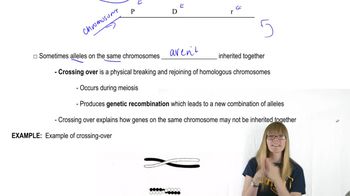
Mapping Overview
Related Videos
Related Practice





