Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
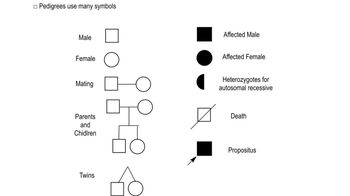
Pedigrees
Problem 19c
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionResearchers examined a family with an interesting distribution of Leigh syndrome symptoms. In this disorder, individuals may show a progressive loss of motor function (ataxia, A) with peripheral neuropathy (PN, meaning impairment of the peripheral nerves). A mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutation that reduces ATPase activity was identified in various tissues of affected individuals. The accompanying table summarizes the presence of symptoms in an extended family.
Person Condition Percent Mitochondria with
Mutation
Proband A and PN >90%
Brother A and PN >90%
Brother Asymptomatic 17%
Mother PN 86%
Maternal uncle PN 85%
Maternal cousin A and PN 90%
Maternal cousin A and PN 91%
Maternal Asymptomatic 56%
grandmother
How can some individuals in the same family show such variation in symptoms? What term, as related to organelle heredity, describes such variation?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
3mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Mitochondrial Inheritance
Mitochondrial inheritance refers to the transmission of genetic material found in mitochondria, which is inherited exclusively from the mother. This type of inheritance can lead to variable expression of traits, as seen in mitochondrial disorders like Leigh syndrome. The severity and presence of symptoms can differ among family members due to the proportion of mutated mtDNA in their cells, which affects cellular energy production.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Organelle Inheritance
Heteroplasmy
Heteroplasmy is the presence of a mixture of more than one type of mitochondrial DNA within a cell or individual. In the context of mitochondrial diseases, individuals may have varying levels of mutated mtDNA, leading to differences in symptom severity. This variation can explain why some family members are symptomatic while others remain asymptomatic despite carrying the same mutation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Organelle DNA Characteristics
Penetrance and Expressivity
Penetrance refers to the proportion of individuals with a specific genotype that actually express the associated phenotype, while expressivity describes the degree to which a genotype is expressed in an individual. In the case of Leigh syndrome, different family members may exhibit varying degrees of symptoms due to differences in penetrance and expressivity, influenced by factors such as environmental conditions and genetic background.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Penetrance and Expressivity

 2:48m
2:48mWatch next
Master Pedigree Symbols with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning