Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
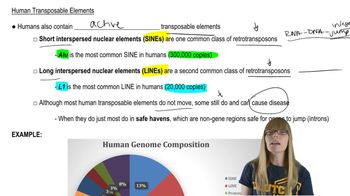
16. Transposable Elements
Transposable Elements in Eukaryotes
Problem 9
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionThe human genome contains a large number of pseudogenes. How would you distinguish whether a particular sequence encodes a gene or a pseudogene? How do pseudogenes arise?
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Gene vs. Pseudogene
A gene is a sequence of DNA that contains the instructions for synthesizing proteins, while a pseudogene is a non-functional segment of DNA that resembles a gene but has lost its ability to code for proteins due to mutations. Distinguishing between the two involves analyzing sequence conservation, presence of regulatory elements, and functional assays to determine if the sequence can produce a functional product.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mapping Genes
Mechanisms of Pseudogene Formation
Pseudogenes can arise through several mechanisms, including gene duplication, where an extra copy of a gene is created and subsequently mutated, or retrotransposition, where mRNA is reverse-transcribed and integrated back into the genome. These processes often lead to the accumulation of mutations that render the pseudogene non-functional.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Formation of Plant Gametes
Functional Analysis Techniques
To determine if a sequence encodes a gene or a pseudogene, researchers employ various functional analysis techniques such as RNA sequencing to assess expression levels, and protein assays to check for functional protein production. These methods help clarify whether a sequence is actively contributing to cellular functions or is merely a remnant of evolutionary history.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Functional Genomics

 3:21m
3:21mWatch next
Master Eukaryotic Transposable Elements with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning