Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage
Mapping Genes
Problem 23b
Textbook Question
Based on our discussion of the potential inaccuracy of mapping (see Figure 5.12), would you revise your answer to Problem 22? If so, how?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Review Problem 22 to understand the original mapping and the genetic distances involved.
Examine Figure 5.12 to identify the potential sources of inaccuracy in genetic mapping, such as interference, double crossovers, or incorrect assumptions about recombination frequency.
Consider how these inaccuracies might affect the genetic distances or order of genes in the original map from Problem 22.
Determine if the inaccuracies suggest a need to adjust the genetic distances or reorder the genes to better reflect the true genetic map.
Propose a revised genetic map or explanation, taking into account the potential inaccuracies identified in Figure 5.12.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
1mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Genetic Mapping
Genetic mapping is the process of determining the location and distance between genes on a chromosome. It involves using markers to identify the relative positions of genes, which can help in understanding inheritance patterns and genetic linkage. Inaccuracies in mapping can arise from recombination events or limitations in the resolution of the mapping techniques used.
Recommended video:
Guided course
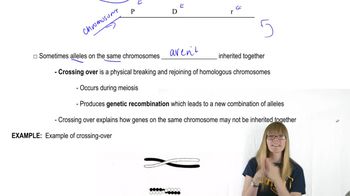
Mapping Overview
Linkage Disequilibrium
Linkage disequilibrium refers to the non-random association of alleles at different loci. It occurs when certain combinations of alleles are inherited together more frequently than would be expected by chance. Understanding linkage disequilibrium is crucial for interpreting genetic maps, as it can affect the accuracy of gene location predictions and the relationships between traits.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chi Square and Linkage
Recombination Frequency
Recombination frequency is a measure of how often recombination occurs between two genes during meiosis. It is used to estimate the distance between genes on a chromosome, with higher frequencies indicating greater distances. Variability in recombination rates can lead to inaccuracies in genetic mapping, making it essential to consider when revising answers based on mapping data.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Recombination after Single Strand Breaks
Related Videos
Related Practice





