Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes
Lac Operon
Problem 12
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionConsider the transcription of genes of the lac operon under two conditions: (1) when both glucose and lactose are present and (2) when glucose is absent and lactose is present. Describe the comparative levels of transcription of lac operon genes under these conditions, and explain the molecular basis for the difference.
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lac Operon Structure and Function
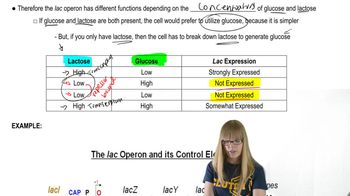
The lac operon is a set of genes in E. coli that are involved in the metabolism of lactose. It consists of three structural genes (lacZ, lacY, and lacA) and regulatory elements that control their expression. The operon is activated in the presence of lactose and repressed when glucose is available, illustrating the concept of gene regulation in response to environmental conditions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lac Operon Overview
Catabolite Repression
Catabolite repression is a regulatory mechanism that prioritizes the use of glucose over other sugars, such as lactose. When glucose is present, it inhibits the production of cyclic AMP (cAMP), which is necessary for the activation of the lac operon. This results in low transcription levels of the lac genes when glucose is available, contrasting with high transcription levels when glucose is absent and lactose is present.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lac Operon Regulation
cAMP and CAP Interaction
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) binds to the catabolite activator protein (CAP), forming a complex that enhances the transcription of the lac operon. In the absence of glucose, cAMP levels rise, allowing the cAMP-CAP complex to bind to the promoter region of the lac operon, facilitating RNA polymerase binding and increasing transcription. This interaction is crucial for understanding how the presence or absence of glucose and lactose affects gene expression.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Interacting Genes Overview

 4:27m
4:27mWatch next
Master Lac Operon Overview with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learning