Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance
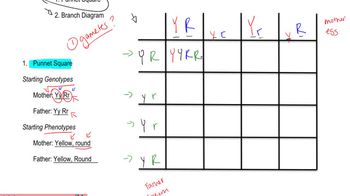
Dihybrid Cross
Problem 16a
Textbook Question
Textbook QuestionPigment in mouse fur is only produced when the C allele is present. Individuals of the cc genotype are white. If color is present, it may be determined by the A, a alleles. AA or Aa results in agouti color, while aa results in black coats. In three crosses between agouti females whose genotypes were unknown and males of the aacc genotype, the following phenotypic ratios were obtained: (1) 8 agouti (2) 9 agouti (3) 4 agouti 8 white 10 black 5 black 10 white
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alleles and Genotypes
Alleles are different forms of a gene that can exist at a specific locus on a chromosome. In this context, the C allele is responsible for pigment production in mouse fur, while the c allele leads to a lack of pigment, resulting in white fur. The genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, such as CC, Cc, or cc, which determines the phenotype, or observable traits, like fur color.
Recommended video:
Guided course

New Alleles and Migration
Phenotypic Ratios
Phenotypic ratios represent the relative frequencies of different phenotypes in the offspring resulting from a genetic cross. In the given crosses, the ratios of agouti, white, and black mice indicate how the alleles interact. Understanding these ratios helps in predicting the outcomes of genetic crosses and in determining the genotypes of the parents based on the observed traits.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Mutations and Phenotypes
Epistasis
Epistasis occurs when the expression of one gene is affected by one or more other genes. In this scenario, the presence of the C allele is necessary for any pigment to be produced, while the A and a alleles determine the specific color if C is present. This interaction illustrates how multiple genes can influence a single trait, complicating the inheritance patterns observed in the offspring.
Recommended video:
Guided course
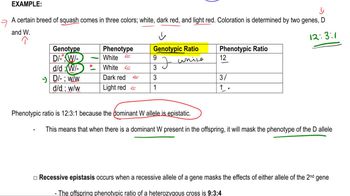
Epistatic Genes
Related Videos
Related Practice