Table of contents
- 1. Introduction to Genetics51m
- 2. Mendel's Laws of Inheritance3h 37m
- 3. Extensions to Mendelian Inheritance2h 41m
- 4. Genetic Mapping and Linkage2h 28m
- 5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses1h 21m
- 6. Chromosomal Variation1h 48m
- 7. DNA and Chromosome Structure56m
- 8. DNA Replication1h 10m
- 9. Mitosis and Meiosis1h 34m
- 10. Transcription1h 0m
- 11. Translation58m
- 12. Gene Regulation in Prokaryotes1h 19m
- 13. Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes44m
- 14. Genetic Control of Development44m
- 15. Genomes and Genomics1h 50m
- 16. Transposable Elements47m
- 17. Mutation, Repair, and Recombination1h 6m
- 18. Molecular Genetic Tools19m
- 19. Cancer Genetics29m
- 20. Quantitative Genetics1h 26m
- 21. Population Genetics50m
- 22. Evolutionary Genetics29m
5. Genetics of Bacteria and Viruses
Bacteriophage Genetics
Problem 22b
Textbook Question
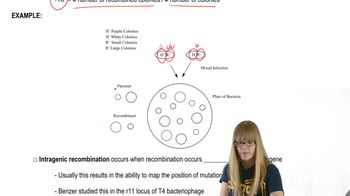
An attribute of growth behavior of eight bacteriophage mutants (1 to 8) is investigated in experiments that establish coinfection by pairs of mutants. The experiments determine whether the mutants complement one another or fail to complement These eight mutants are known to result from point mutation. The results of the complementation tests are shown below.

New mutation 10 fails to complement mutants 1, 4, 5, 6, 8, and 9. Mutant 10 forms wild-type recombinants with mutants 1, 5, and 6, but not with mutants 4 and 8. Mutant 9 and mutant 10 form wild-type recombinants. What kind of mutation is mutant 10? Explain your reasoning.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the mutants that fail to complement with mutant 10: 1, 4, 5, 6, 8, and 9.
Note that mutant 10 forms wild-type recombinants with mutants 1, 5, 6, and 9, but not with mutants 4 and 8.
Understand that complementation occurs when two mutations are in different genes, allowing for a functional product to be produced.
Recombination forming wild-type indicates that the mutations are in different locations within the same gene.
Conclude that mutant 10 is likely an intragenic mutation, as it fails to complement with certain mutants but can recombine to form wild-type with others.
Recommended similar problem, with video answer:
 Verified Solution
Verified SolutionThis video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
2mPlay a video:
Was this helpful?

 3:44m
3:44mWatch next
Master Plaques and Experiments with a bite sized video explanation from Kylia Goodner
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice